Intended Data Use Statement (IDU)
Objectives of the Proposed Research:
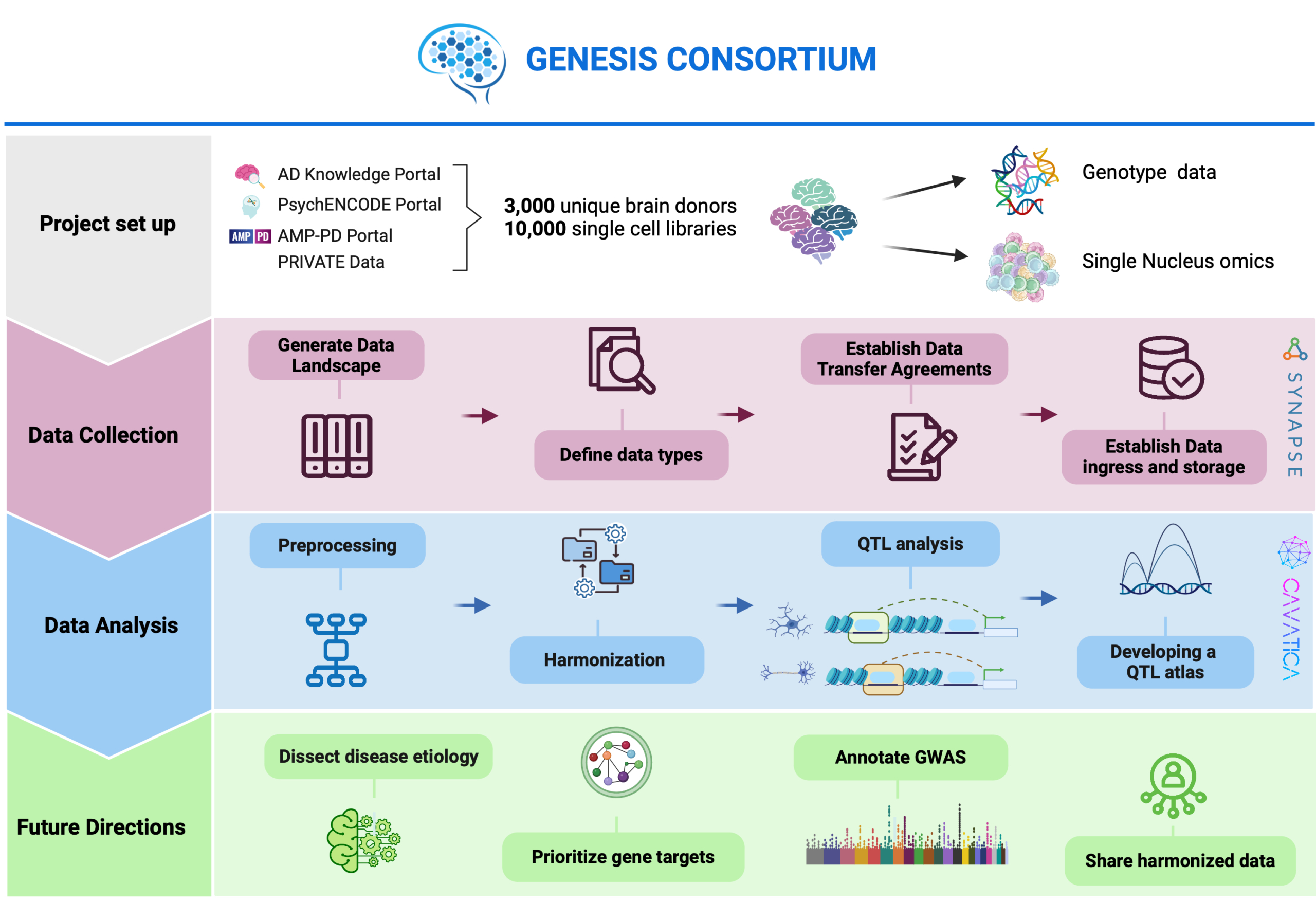
The primary objective of this research is to construct a comprehensive cell type-specific quantitative trait loci (QTL) atlas for the human brain. This atlas will be instrumental in identifying genetically driven gene dysregulation mechanisms in serious mental and neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and schizophrenia. By integrating risk loci with QTLs for molecular traits such as gene expression and epigenome regulation in human brain tissue, we aim to enhance our mechanistic understanding of these disorders. Additionally, the project seeks to prioritize significant genes and molecular pathways, provide a valuable resource for ongoing and future genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and establish a standardized mechanism for data sharing and harmonization across consortia and projects.
Study Design and Analysis Plan:
Consortium Formation
The GENESIS Consortium will be established, combining resources from over 10,000 single-cell libraries derived from more than 3,000 unique brain donors. This consortium will integrate expertise in single-cell biology, neuroscience, statistical genetics, and machine learning.
Data Collection and Harmonization
We will collect single-cell data and integrate it with QTLs for molecular traits, including gene expression and epigenome regulation. This data will be harmonized using the Synapse Data Platform by Sage Bionetworks, an NIH-Designated Generalist Repository. The platform will facilitate data validation against metadata and data standards, and harmonization for downstream analysis.
QTL Generation and Analysis
The harmonized data will be used to perform QTL analysis, identifying cell type-specific QTLs. To ensure reproducibility and transparency, data processing and analysis will be conducted using CAVATICA by Seven Bridges, a secure, scalable, and extendable data commons platform.
Downstream Analysis and Resource Creation
We will construct a cell type-specific QTL atlas for the human brain. This atlas will be used to derive genetically driven gene dysregulation mechanisms in serious mental and neurological disorders.
Resource Distribution and Data Sharing
The preprocessed and harmonized single-nucleus brain omics data will be shared with the scientific community. This will enable researchers to address various biologically-driven questions beyond the scope of this project.
Outcome and Future Directions
Upon completion, the project will provide a valuable resource for understanding the mechanisms of neurological and psychiatric disorders. It will support ongoing and future GWAS by integrating cell type-specific QTL data, allowing for more precise identification of risk loci. Additionally, the established protocols for data sharing and harmonization will set the stage for future single-cell mega-analyses and meta-analyses.
In summary, the GENESIS Consortium aims to overcome the limitations of previous integrative analyses by focusing on cell type-specific QTLs using single-cell data. This approach will provide deeper insights into the biological mechanisms of serious mental and neurological disorders, prioritize significant genes and pathways, and facilitate data sharing and harmonization within the scientific community.